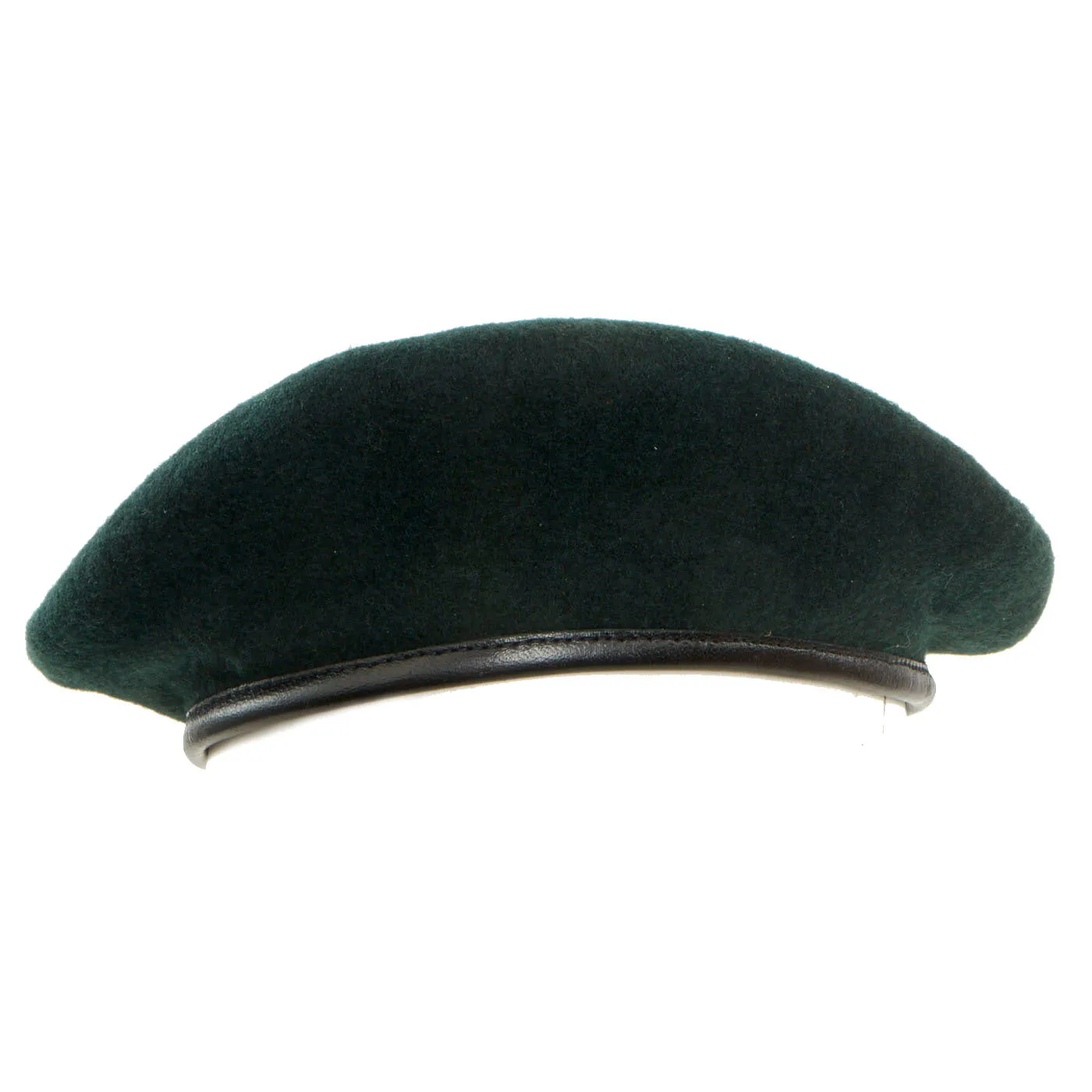
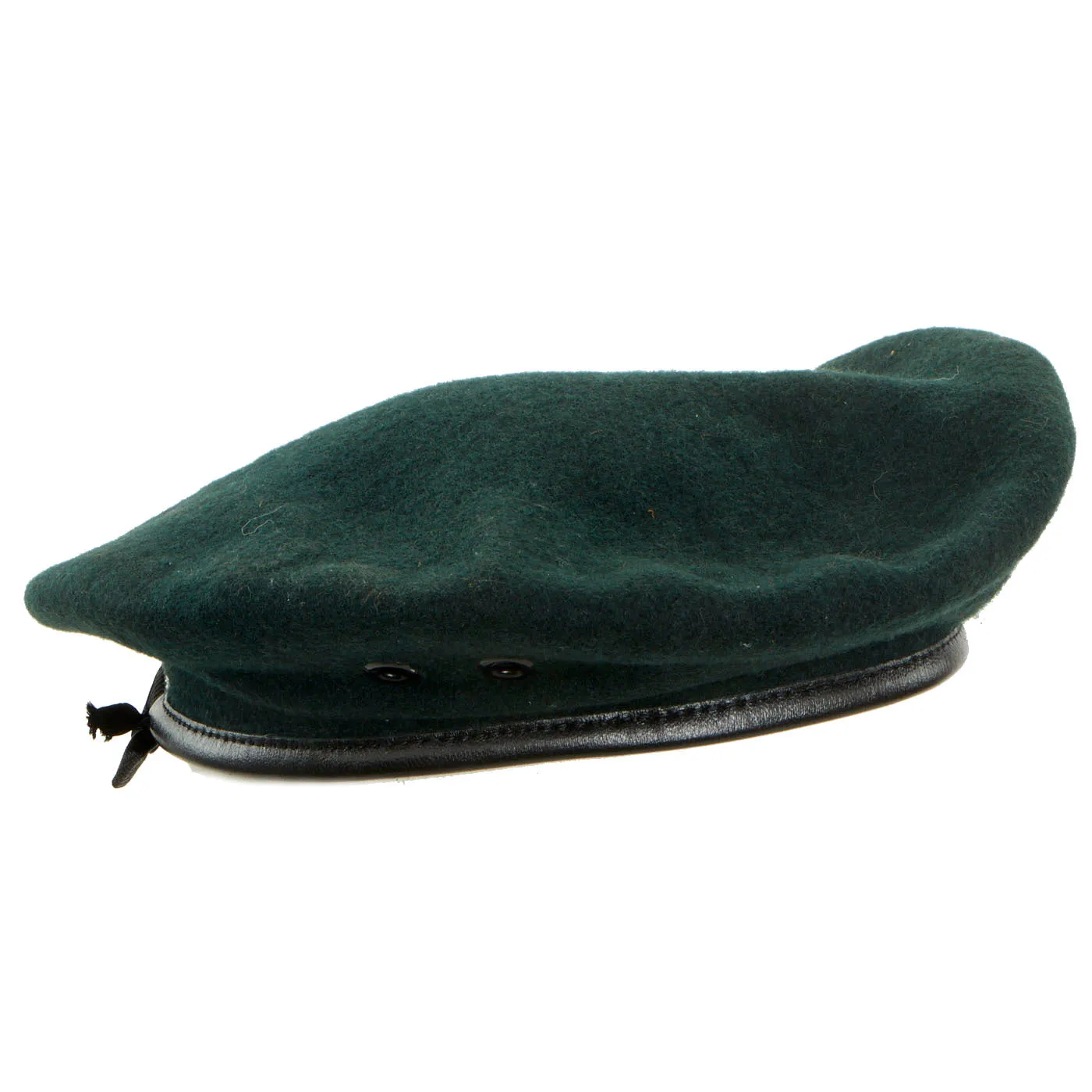
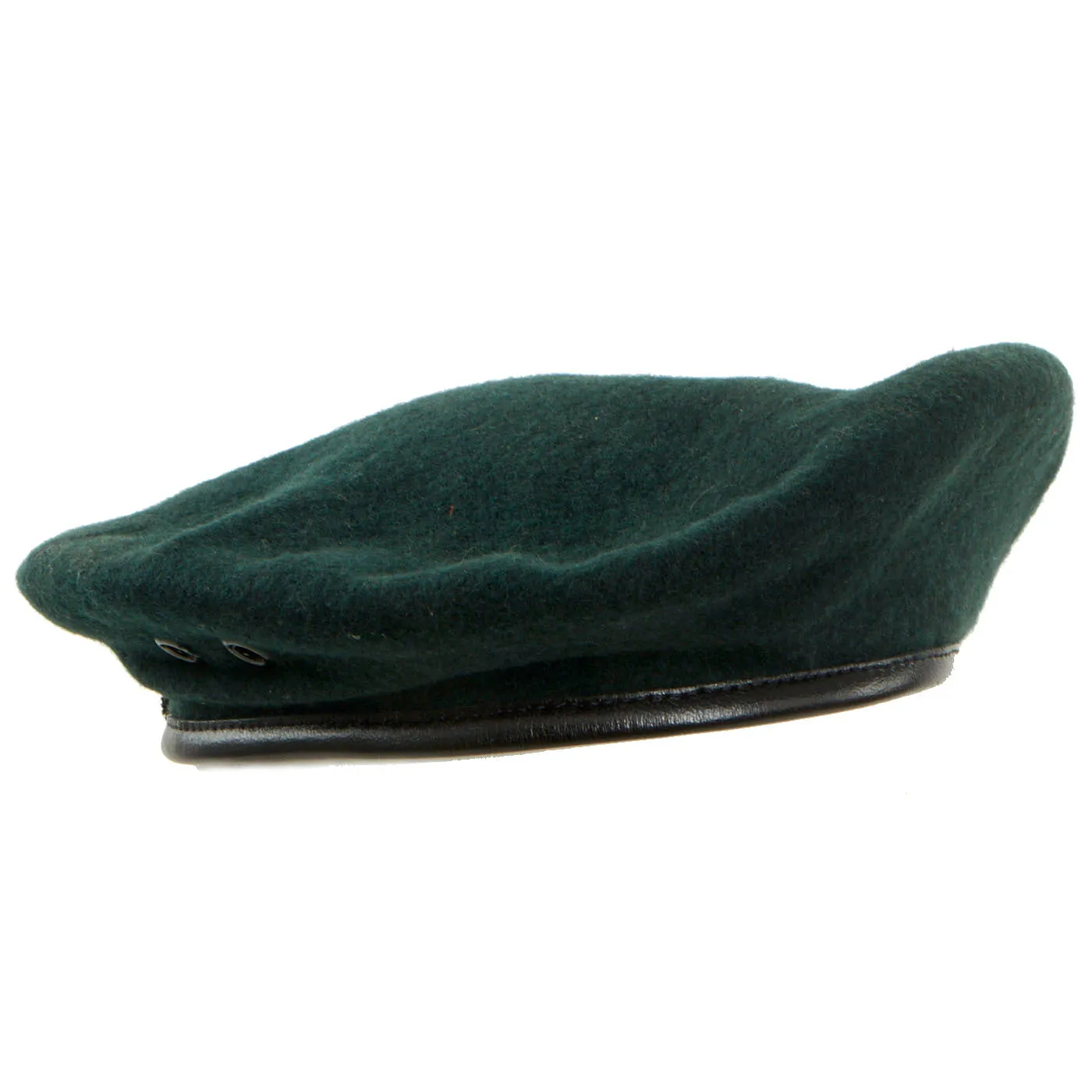
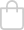
Original Item: Only One Available. Now this is a beauty! A mint condition, unissued “Rifle Green” Special Forces beret dated from 1965. This is an untouched example and does not display any signs of ever having any badges, flashes or insignia affixed to it. It is a size 6 ⅞ and still has the original white stamping visible on the inside.
BERET, MAN’S, WOOL
RIFLE GREEN
DSA 100 1774
6615-082-5644 (Double stamped, hard to read)
As stated, it is in excellent unworn and complete condition. It is worth of any Vietnam War Special Forces collections!
United States Army Special Forces
The United States Army Special Forces, colloquially known as the "Green Berets" due to their distinctive service headgear, are a special operations force of the United States Army that are designed to deploy and execute nine doctrinal missions: unconventional warfare, foreign internal defense, direct action, counter-insurgency, special reconnaissance, counter-terrorism, information operations, counterproliferation of weapons of mass destruction, and security force assistance. The first two missions, unconventional warfare and foreign internal defenses, emphasize language, cultural, and training skills in working with foreign troops. Other Special Forces missions, known as secondary missions, include: combat search and rescue (CSAR), counter-narcotics, hostage rescue, humanitarian assistance, humanitarian demining, information operations, peacekeeping, and manhunts. Other components of the United States Special Operations Command (USSOCOM) or other U.S. government activities may also specialize in these secondary missions. The Special Forces conduct these missions via seven geographically focused groups. Many of their operational techniques are classified, but some nonfiction works and doctrinal manuals are available.
As special operations units, Special Forces are not necessarily under the command authority of the ground commanders in those countries. Instead, while in theater, SF units may report directly to a geographic combatant command, USSOCOM, or other command authorities. The Central Intelligence Agency's (CIA) highly secretive Special Activities Center (formerly known as the "Special Activities Division") and more specifically its Special Operations Group (SOG) recruits from the U.S. Army's Special Forces. Joint CIA–Army Special Forces operations go back to the MACV-SOG branch during the Vietnam War. The cooperation still exists today and was seen in the War in Afghanistan.
The Special Forces traces its roots as the Army's premier proponent of unconventional warfare from purpose-formed special operations units like the Alamo Scouts, Philippine guerrillas, First Special Service Force, and the Operational Groups (OGs) of the Office of Strategic Services (OSS). Although the OSS was not an Army organization, many Army personnel were assigned to the OSS and later used their experiences to influence the forming of Special Forces.
During the Korean War, individuals such as former Philippine guerrilla commanders Col. Wendell Fertig and Lt. Col. Russell W. Volckmann used their wartime experience to formulate the doctrine of unconventional warfare that became the cornerstone of the Special Forces.
In 1951, Major General Robert A. McClure chose former OSS member Colonel Aaron Bank as Operations Branch Chief of the Special Operations Division of the Psychological Warfare Staff (OCPW) in the Pentagon.
In June 1952, the 10th Special Forces Group (Airborne) was formed under Col. Aaron Bank, soon after the establishment of the Psychological Warfare School, which ultimately became today's John F. Kennedy Special Warfare Center and School. The 10th Special Forces Group (Airborne) was split, with the cadre that kept the designation 10th SFG deployed to Bad Tölz, Germany, in September 1953. The remaining cadre at Fort Bragg formed the 77th Special Forces Group, which in May 1960 was reorganized and designated as today's 7th Special Forces Group.
Since their establishment in 1952, Special Forces soldiers have operated in Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, North Vietnam, Guatemala, Nicaragua, El Salvador, Colombia, Panama, Haiti, Somalia, Bosnia, Kosovo, 1st Gulf War, Afghanistan, Iraq, the Philippines, Syria, Yemen, Niger and, in an FID role, East Africa.
The Special Forces branch was established as a basic branch of the United States Army on 9 April 1987 by Department of the Army General Order No. 35.